|
1. |
Check the crankshaft bearing oil clearance.
|
(1) |
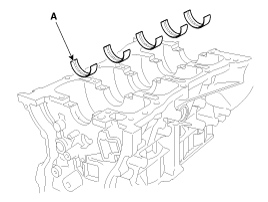
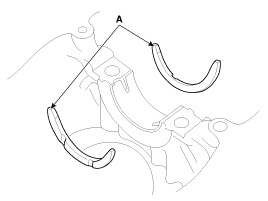
To check main bearing-to-journal oil clearance,
remove the main caps and bearing halves.
|
|
(2) |
Clean each main journal and bearing half
with a clean shop tower.
|
|
(3) |
Place one strip of plastigage across each
main journal.
|
|
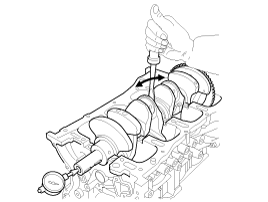
(4) |
Reinstall the bearings and caps, then torque
the bolts.
Tightening
torque :
14.7 N.m (1.5 kgf.m, 10.8 lb-ft)
+ 27.5 ~ 31.4 N.m (2.8 ~ 3.2 kgf.m, 20.3 ~ 23.1 lb-ft)
+ 120 ~ 125°
|
|
Do not turn the crankshaft.
|
|
|
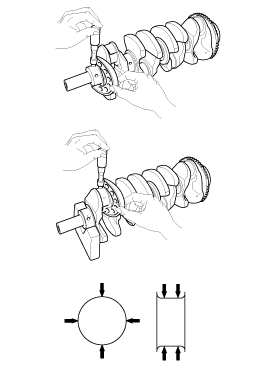
(5) |
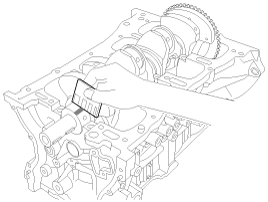
Remove the cap and bearing again, and measure
the widest part of the plastigage.
Standard
oil clearance :
0.020 ~ 0.038 mm (0.00079 ~ 0.00150
in.)
|
|
|
(6) |
If the plastigage measures too wide or too
narrow, remove the upper half of the bearing, install a new,
complete bearing with the same color mark (select the color
as shown in the next column), and recheck the clearance.
|
Do not file, shim, or scrape the
bearings or the caps to adjust clearance.
|
|
|
(7) |
If the plastigage shows the clearance is
still incorrect, try the next larger or smaller bearing (the
color listed above or below that one), and check clearance again.
|
If the proper clearance cannot be
obtained by using the appropriate larger or smaller
bearings, replace the crankshaft and start over.
|
|
If the marks are indecipherable because
of an accumulation of dirt and dust, do not scrub them
with a wire brush or scraper. Clean them only with solvent
or detergent.
|
|
Crankshaft Bore Identification Mark
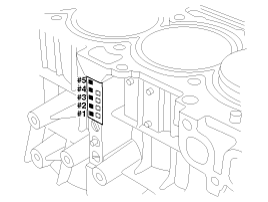
Letters have been stamped on the block as a mark
for the size of each of the 5 main journal bores.
Use them, and the numbers or bar stamped on the crank
(marks for main journal size), to choose the correct bearings.
Cylinder Block Specifications
Calss
|
Mark
|
Inside Diameter
|
a
|
A
|
56.000 ~ 56.006 mm
(2.20472 ~ 2.20496 in.)
|
b
|
B
|
56.006 ~ 56.012 mm
(2.20496 ~ 2.20519 in.)
|
c
|
C
|
56.012 ~ 56.018 mm
(2.20519 ~ 2.20543 in.)
|
Crankshaft Journal Identification Mark
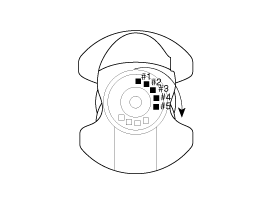
|
Conform to read stamping order as shown arrow
direction from #1.
|
Crankshaft Specifications
Class
|
Mark
|
Outside Diameter Of
Journal
|
I
|
1
|
51.954 ~ 51.960 mm
(2.04543 ~ 2.04567 in.)
|
II
|
2
|
51.948 ~ 51.954 mm
(2.04519 ~ 2.04543 in.)
|
III
|
3
|
51.942 ~ 51.948 mm
(2.04496 ~ 2.04519 in.)
|
Crankshaft Bearing Identification Mark
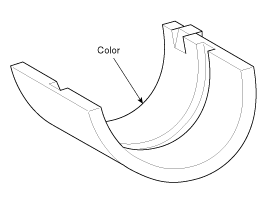
Crankshaft Bearing Specifications
Class
|
Mark
|
Thickness Of Bearing
|
AA
|
Blue
|
2.026 ~ 2.029 mm
(0.07976 ~ 0.07988 in.)
|
A
|
Black
|
2.023 ~ 2.026 mm
(0.07965 ~ 0.07976 in.)
|
B
|
None
|
2.020 ~ 2.023 mm
(0.07953 ~ 0.07965 in.)
|
C
|
Green
|
2.017 ~ 2.020 mm
(0.07941 ~ 0.7953 in.)
|
D
|
Yellow
|
2.014 ~ 2.017 mm
(0.07929 ~ 0.07941 in.)
|
Selection Chart For Crankshaft Bearings
Crankshaft Identification
Mark
|
Crankshaft Bore Identification
Mark
|
Assembling Classification
Of Bearing
|
I (1)
|
a (A)
|
D (Yellow)
|
b (B)
|
C (Green)
|
c (C)
|
B (None)
|
II (2)
|
a (A)
|
C (Green)
|
b (B)
|
B (None)
|
c (C)
|
A (Black)
|
III (3)
|
a (A)
|
B (None)
|
b (B)
|
A (Black)
|
c (C)
|
AA (Blue)
|
|
 Hyundai Santa Fe: Crankshaft. Repair procedures
Hyundai Santa Fe: Crankshaft. Repair procedures Crankshaft. Components and Components Location
Crankshaft. Components and Components Location Cooling System
Cooling System